


Hanging valley: A former glacial tributary valley that enters a larger glacial valley above its base, high up on the valley wall.

Hard water: Water that contains sufficient dissolved calcium and magnesium to cause a carbonate scale to form when the water is boiled or to prevent the sudsing of soap.

HEAT:If a temperature difference exists between two points heat will flow from the point at the higher temperature to the point at the lower temperature. This flow will continue until equilibrium has been reached

Heat conduction: The transfer of the rapid vibrational energy of atoms and molecules, which constitutes heat energy, through the mechanism of atomic or molecular impact.

Heat engine: A device that transfers heat from a place of high temperature to a place of lower temperature and does mechanical work in the process.

Hill: A natural land elevation, usually less than 1000 feet above its surroundings, with a rounded outline. The distinction between hill and mountain depends on the locality.
Hogback: A formation similar to a Cuesta in that it is a ridge formed by slower erosion of hard strata, but having two steep, equally inclined slopes.

Hooke's Law: The principle that the stress within a solid is proportional to the strain. It holds only for strains of a few percent or less.

Hornfels: A high-temperature, low-pressure metamorphic rock of uniform grain size showing no foliation. Usually formed by contact metamorphism.

Horst: An elongate, elevated block of crust forming a ridge or plateau, typically bounded by parallel, outward-dipping normal faults.

Hot spring: A spring whose waters are above both human body and soil temperature as a result of plutonism at depth.

Humus: The decayed part of the organic matter in a soil.

Hydration: A chemical reaction, usually in weathering, which adds water or OH to a mineral structure.

Hydraulic conductivity: A measure of the permeability of a rock or soil: the volume of flow through a unit surface in unit time with unit hydraulic pressure difference as the driving force.

Hydrocarbon: An organic chemical compound made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms arranged in chains or rings.

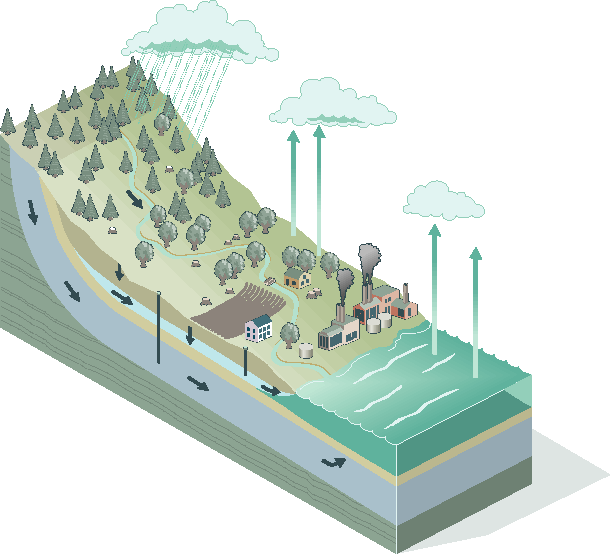
Hydrologic cycle: The cyclical movement of water from the ocean to the atmosphere, through rain to the surface, through runoff and groundwater to streams, and back to the sea.
Hydrology: The science of that part of the hydrologic cycle between rain and return to the sea; the study of water on and within the land.
_de_DSC05454.jpg)
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario