
"Hi there!...Wait a few minutes in order to carge the page. you will find words, meanings, images and videos. in the left side you will find a translator and a virtual radius in order to let you listen the music in english. Thank you for visiting!





ADJECTIVE:The part of speech that modifies a noun or other sustantive. it is a word used tu describe people, animal and objects
Example: big- small

ADVERB: It is a word that changes the verb and/or the adjective

Alkali metal: A strongly basic metal like potassium or sodium.

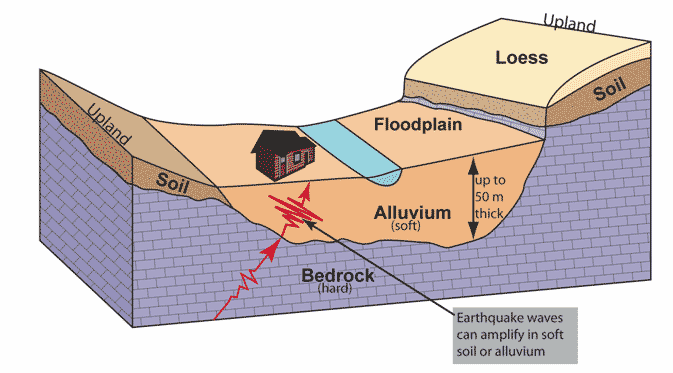
Alluvium: Unconsolidated terrestrial sediment composed of sorted or unsorted sand, gravel, and clay that has been deposited by water
Angular unconformity: An unconformity in which the bedding planes of the rocks above and below are not parallel.ular unconformity
Anthracite: The most highly metamorphosed form of coal, containing 92 to 98 percent of fixed carbon. It is black, hard, and glassy.

Aquifer: A permeable formation that stores and transmits groundwater in sufficient quantity to supply wells.

ARCHIMIDES:was a Greek mathematician, physicist,engineer, inventor, and astronomer. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientist in classical antiquity.

Arkose: A variety of sandstone containing abundant feldspar and quartz, frequently in angular, poorly sorted grains.

Artesian well: A well that penetrates an aquiclude to reach an aquifer containing water under pressure. Thus water in the well rises above the surrounding water table

ARTICLES: word used before nouns.In English the definite article is the, the indefinite article is a or an, and their force is generally to impart specificity to the noun or to single out the referent from the class named by the noun.


ATOLL: A continuous or broken circle of coral reef and low coral islands surrounding a central lagoon

AXIS:The line, real or imaginary, passing through the center of an object about which it could rotate; a point of reference.












































_de_DSC05454.jpg)