


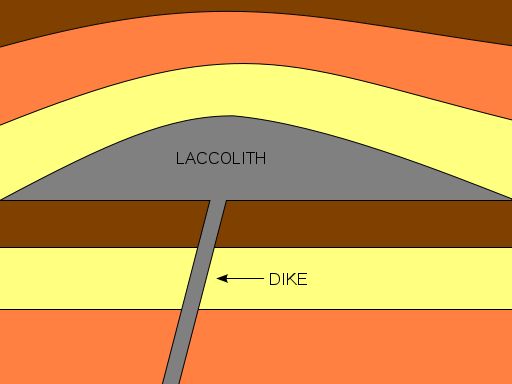
Laccolith: A sill-like igneous intrusion that forces apart two strata and forms a round, lens-shaped body many times wider than it is thick.
Lahar: A mudflow of unconsolidated volcanic ash, dust, breccia, and boulders mixed with rain or the water of a lake displaced by a lava flow.

Landslide: The rapid downslope movement of soil and rock material, often lubricated by groundwater, over a basal shear zone; also the tongue of stationary material deposited by such an event.

Lapilli: A fragment of volcanic rock formed when magma is ejected into the air by expanding gases. The size of the fragments ranges from sand- to cobble-size.
![]()
Lateral moraine: A moraine formed along the side of a valley glacier and composed of rock scraped off or fallen from the valley sides.

Lava: Magma or molten rock that has reached the surface.

Leaching: The removal of elements from a soil by dissolution in water moving downward in the ground.

LEVER: is a rigid object that is used with an appropriate fulcrum or pivot point to multiply the mechanical force that can be applied to another object.

Limestone: A sedimentary rock composed principally of calcium carbonate (CaCO2), usually as the mineral calcite.

Lineation: Any linear arrangement of features found in a rock.

Liquid:A fluid (such as water) that has no independent shape but has a definite volume and does not expand indefinitely and that is slightly compressible.

Lithification: The processes that convert a sediment into a sedimentary rock.

Lithology: The systematic description of rocks, in terms of mineral composition and texture.

Lithosphere: The outer, rigid shell of the Earth, situated above the asthenosphere and containing the crust, continents, and plates.

Lopolith: A large laccolith that is bowl-shaped and depressed in the center, possibly by subsidence of an emptied magma chamber beneath the intrusion.

Lowland: Land of general low relief at the lower levels of regional elevation.

Low-velocity zone: A region in the Earth, especially a planar layer that has lower seismic-wave velocities than the region immediately above it.
Luster: The general textural impression of a mineral surface, given by the light reflected from it. Terms such as metallic, submetallic are standardized but subjective.

_de_DSC05454.jpg)
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario